How Glacier Melting Threatens Water Security Globally
Glacier melting threatens global water security by reducing freshwater supplies, increasing sea levels, and disrupting ecosystems, necessitating immediate sustainable adaptation strategies to safeguard communities and the environment.
Glacier melting is becoming a crisis that affects billions, threatening their water security. Have you ever wondered how this impacts our future?
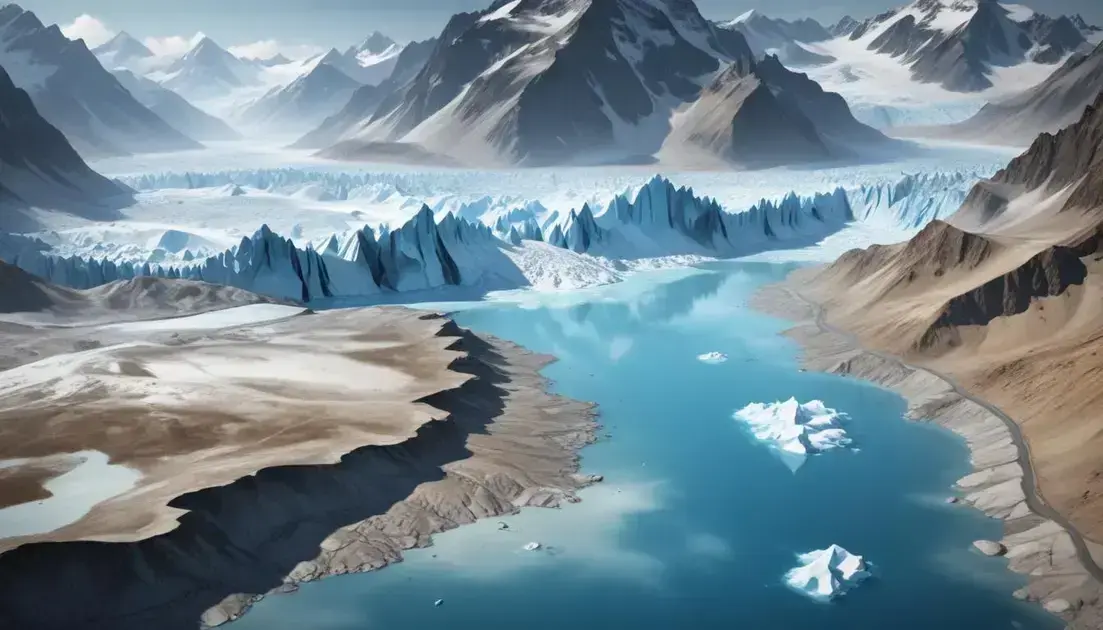
The impact of glacier melting on global water supplies
The impact of glacier melting on global water supplies is profound and alarming. As glaciers continue to shrink due to rising temperatures, they pose a serious threat to freshwater availability for millions of people. Glaciers act as natural reservoirs, slowly releasing water into rivers and streams that feed countless communities. With their retreat, we are witnessing a decline in these critical water sources.
Particularly in regions heavily reliant on glacial melt, such as the Himalayas and the Andes, the situation is dire. Many populations depend on this seasonal meltwater for drinking, farming, and industry. As glaciers disappear, there is a substantial risk of water scarcity, leading to agricultural challenges and heightened competition for increasingly precious water resources.
Moreover, the ramifications extend beyond immediate water supply issues. The alteration in water flow patterns may lead to flooding in some areas while creating drought conditions elsewhere. This unpredictability complicates water management strategies and amplifies the need for sustainable practices to adapt to the changing environment.
Collectively, the global response to glacier melting demands urgent attention. Policymakers and communities must collaborate to implement protective measures, ensuring water security amidst this climate crisis.
Communities at risk: Water insecurity and agriculture
Communities at risk due to water insecurity experience profound challenges, especially in agricultural areas. As glacier melting leads to dwindling water supplies, these communities face a dual threat: decreased availability of freshwater for irrigation and increased competition for water resources.
The reliance on glacial meltwater for crop production makes many farmers vulnerable to shifts in water availability. Without sufficient water, crop yields decline, threatening food security and livelihoods. This situation presents a worrying trend, as farmers struggle to adapt to changing conditions.
Moreover, water insecurity can exacerbate social tensions. As local farmers compete for the same limited water resources, conflicts may arise, further complicating the already precarious situation. Communities that depend heavily on agriculture for economic stability are thus caught in a cycle of vulnerability and scarcity.
Sustainable farming practices and effective water management strategies are essential to mitigate these risks. Innovations in irrigation technology and community teamwork can enhance water use efficiency, preserving what little is available. Therefore, addressing water insecurity is not just a local issue, but a global imperative that requires concerted action.
Climate feedback loops from glacial retreat
Climate feedback loops resulting from glacial retreat represent a significant challenge in understanding climate change. As glaciers melt, they expose darker land surfaces that absorb more sunlight, increasing local temperatures. This process creates a dangerous cycle that accelerates glacial melting even further.
When large ice bodies, like glaciers, disappear, they contribute to rising sea levels. This rise alters ocean temperatures and contributes to more extreme weather patterns, creating additional stress on ecosystems and human settlements. The melting glaciers also release trapped greenhouse gases, like methane and carbon dioxide, which can enhance the greenhouse effect and further warm the planet.
The consequences extend beyond the immediate regions affected by glacier loss, influencing global weather systems. These changes can cause longer droughts, stronger storms, and increased flooding in various regions. Thus, the connections between glacial retreat and climate feedback loops showcase the complex interplay of environmental factors at work.
Addressing these feedback loops requires comprehensive climate action, focusing on reducing emissions and implementing sustainable practices. By tackling the root causes of climate change, societies can slow down these feedback cycles and mitigate the broader impacts on our planet.
The call for sustainable adaptation strategies
The urgency of addressing climate change has amplified the call for sustainable adaptation strategies. As communities around the world face the ramifications of glacial melting and water scarcity, it becomes crucial to implement solutions that can withstand environmental shifts.
One effective approach is the adoption of integrated water resource management. This method encourages the efficient use of available water, promoting conservation and alternative sources such as rainwater harvesting. By harnessing multiple water sources, communities can enhance their resilience against changing climatic conditions.
Additionally, sustainable agricultural practices must be prioritized. Techniques like crop rotation, conservation tillage, and sustainable irrigation can markedly improve soil health and reduce water use. These practices not only sustain food production but also preserve essential ecosystems.
Furthermore, investing in education and community engagement is vital. Informing residents about sustainable practices fosters a culture of resilience and collective responsibility. When communities are empowered to participate in these initiatives, they are better equipped to adapt to and mitigate the effects of climate change.
Global implications of disappearing glaciers
The global implications of disappearing glaciers are far-reaching and significant. As glaciers melt at unprecedented rates due to climate change, entire ecosystems and communities are affected. These ice masses are vital sources of freshwater for billions of people around the world. When they diminish, the availability of water for drinking, agriculture, and industry is severely impacted.
Rising sea levels are another critical consequence of glacial retreat. The melting ice contributes directly to elevated sea levels, threatening coastal cities and low-lying areas. This can lead to increased flooding and erosion, displacing communities and causing substantial economic loss. In particular, island nations face an existential threat from the encroaching seas.
Moreover, the loss of glaciers disrupts natural habitats. Many species that depend on these cold-water ecosystems find it increasingly challenging to survive. The alteration of these environments can lead to biodiversity loss, impacting food chains and local economies that rely on fishing and tourism.
Addressing these implications requires global cooperation and immediate action. Reducing greenhouse gas emissions and investing in renewable energy sources are essential steps to mitigate climate change and protect the world’s glaciers. Only through collective efforts can we safeguard these vital resources for future generations.
In Summary: The Urgent Need for Action
The impacts of climate change, especially through the melting of glaciers, are critical to our planet’s health and humanity’s future. With the loss of glaciers, we face threats like water insecurity, rising sea levels, and biodiversity loss.
It is essential that we adopt sustainable adaptation strategies and work collectively to mitigate these effects. Investing in renewable energy and protecting natural resources can help combat climate change and protect vulnerable communities.
By understanding and addressing the implications of disappearing glaciers, we can take steps toward a more sustainable future. Our actions today will determine the resources and environment available for generations to come.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the main causes of glacier melting?
Glacier melting is primarily caused by rising global temperatures due to climate change, mainly driven by greenhouse gas emissions from human activities.
How does glacier melting affect water supply?
As glaciers melt, they initially increase water supply but eventually lead to water scarcity as the glaciers recede, threatening freshwater access for many communities.
What are the environmental impacts of disappearing glaciers?
Disappearing glaciers result in rising sea levels, loss of habitat for wildlife, and increased natural disasters, disrupting local and global ecosystems.
How can communities adapt to climate change?
Communities can adapt by implementing sustainable practices like water conservation, renewable energy use, and engaging in education about climate resilience.
What actions can be taken to mitigate climate change?
To mitigate climate change, we can reduce greenhouse gas emissions, invest in clean energy, and support policies that promote environmental sustainability.
Why is it important to address glacier loss now?
Addressing glacier loss is crucial because delaying action will exacerbate water shortages, increase flooding risks, and harm biodiversity, affecting future generations.